Russian Salon Dog Colors
Red, Fawn, Cream.
The breed has several options for a completely red color. They are caused by genes located at locus A (at, ay, aw) and at the locus E (Ee). All of them belong to the red range and are bred with each other and with spotted redheads.
Variants of the red color range:
1) Dominant red without darkening: dogs look completely red. Determined by the presence of a gene ay..
With this color, there can be:
- any pigmentation of the nose, lips, eyelids, claws, pads, skin (black, brown, blue, isabella);
- any shade of red;
– mask;
— podlas.
Puppies are born red, registered as "red" (rich red) or "fawn" (pale red) depending on the saturation of the red shade. If a puppy has a mask and / or undercoat, they are not included in the name of the color.
A y - red dogs with black pigment have a black nose, as well as black lips, eyelids, claws, pads, dark brown eyes.
And in -red dogs with brown pigment have a brown nose, as well as brown lips, eyelids, claws, pads, brown and light brown eyes. The shade of brown can be more or less saturated.
And in -red dogs with blue pigment have a gray nose, as well as gray lips, eyelids, claws, pads, brown and light brown eyes. The shade of gray can be more or less saturated.
And in -red dogs with isabella pigment have a grayish-pinkish-brownish nose and approximately the same shade of lips, eyelids, claws, pads, brown and light brown eyes. The shade of the nose, eyelids, etc. can be more or less saturated.
Dogs of this color must have at least one " E" gene in the E locus
Genotype variants:
Genotype variants:
- A y/A y is a red dog;
- A y /A y is a red dog, carries the sable color gene;
- A y/a w is a red dog, carries the zoning gene;
- A y/a t is a red dog, carries the tan gene;
- A y/a is a red dog, carries the recessive black color gene.


2) Dominant red with darkening: the base of the hair is red; the rest of the hair is darkened.
Determined by the presence of a gene Ay. This color is also called "sable", "red with black/red with brown/red with blue/red with isabella", "murrug".
This color can be:
- any pigmentation of the nose, lips, eyelids, claws, pads, skin (black / brown / blue / isabella),
- any shade of red,
- darkening is manifested to any degree: only the tip, half a hair, almost a whole hair,
- there can be separate completely darkened hairs and whole strands (black / brown / blue / isabella) on the ears, head, tail,
- there is completely red hair (on the head, limbs, throat, etc.),
- a mask,
- darkening on the muzzle like a mask,
- an undercoat.
Puppies are born with a darkening of the coat to a greater or lesser extent. As they grow, the darkened ends of the hair grow out and are cut off, as a result of which the darkening can disappear completely and the dog will become either entirely red or with darkening in certain places (for example, on the tail). If the red part of the color is a rich red shade, the puppies are registered as "red". If the red part of the color is light red, they are registered as "fawn".
Ay/ay- Red dogs with black pigment have a black nose lobe, as well as black lips, eyelids, claws, pads, dark brown eyes.
Ay,bb-Red dogs with brown pigment have a brown nose lobe, as well as brown lips, eyelids, claws, pads, brown and light brown eyes. The shade of brown can be more or less saturated.
Ay,dd- Red dogs with blue pigment have a gray nose lobe, as well as gray lips, eyelids, claws, pads, brown and light brown eyes. The shade of gray can be more or less saturated.
Ay,bb,dd- Red dogs with isabella pigment have a grayish-pinkish-brownish nose and lips, eyelids, claws, pads, brown and light brown eyes of about the same shade. The shade of the nose lobe, eyelids, etc. can be more or less saturated.
Dogs of this color must have at least one "E" gene at the E locus.
red with black shading
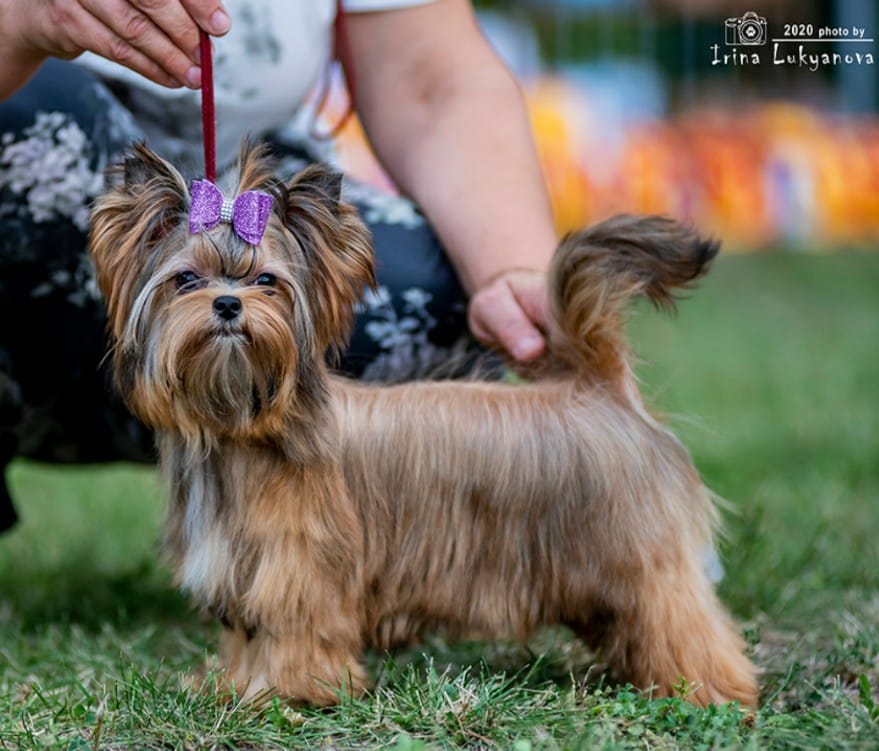

red with brown shading

Red dog with darkening
on tail and whiskers

Red dog with darkening
on the ears and with a mask
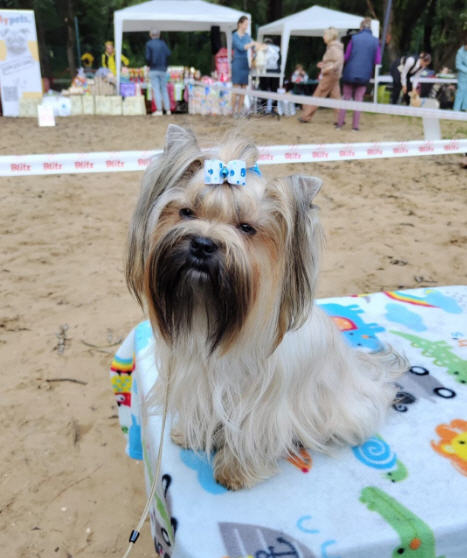

sable dog
bright red = red

Sable dog light red = fawn
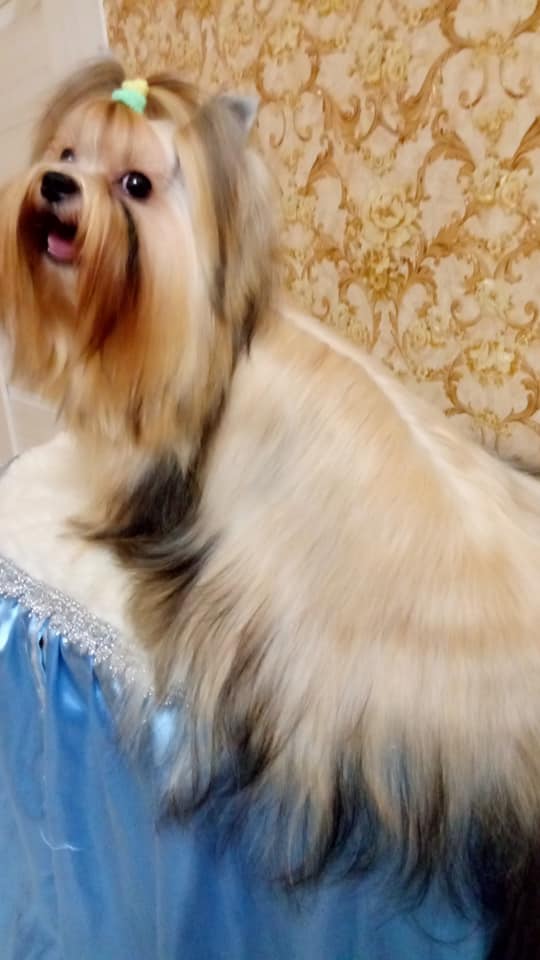

The darkened part of the hair (black/brown/blue/Isabella) can be pronounced or faint.
Sable dog
with bright shade (Red)
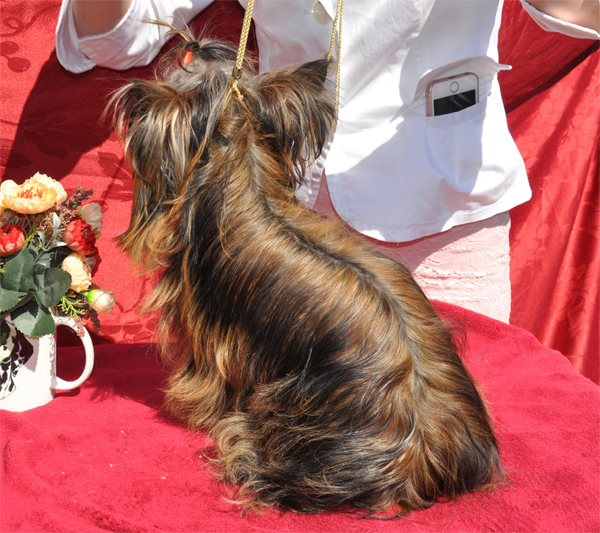

Sable dog
with dim shade (Fawn)

Genotype variants:
— Ay/Ay - sable dog;
— Ay/Aw – sable dog, carries the zonarity gene;
— Ay/at - sable dog, carries the tan gene;
— Ay/a is a sable dog that carries the gene for recessive black color.
3) Zonal color: the hair is colored in zones. It is determined by the presence of the aw gene.
With this color, there can be:
- any pigmentation of the nose lobe, eyelids, claws, pads, skin (black, brown, blue, isabella),
- zones on the hair alternate individually, i.e. they can be arbitrarily wide or narrow,
- there may be areas without pigment on the hair, which gives the appropriate shade,
- red zones can have any shade of red.
Puppies are born similar to sables. But unlike the latter, the eumelanin zone (black/brown/blue/isabella) never disappears with age. As the coat grows, the dog may look either redder or darker. If the red part of the color is a rich red hue, puppies are described as "redheads". If the red part of the color is light red, they are described as "fawn". Dogs of this color must have at least one "E" gene at the E locus.
In the process of breeding mermaids, no breeds were used that could bring zonal color. But since dogs of unknown origin participated in the breeding, they could theoretically bring zonal color to the breed. Since zonarity can be disguised as sable color (with very narrow eumelanin zones), there is a possibility that this color is in the breed. However, it is not necessary to cultivate it, because with zonal coloring, darkened zones make the color dirty.
Genotype variants:
— aw/aw - zonar dog;
— aw/at – zonary dog, carries the tan gene;
— aw/a is a zonal dog, carries the gene for recessive black color.
4) Recessive Red Color: An all-red dog without a single black/brown/blue/isabella hair. It is determined by the presence of two genes for "ee"
With this color, there can be:
- any pigmentation of the nose lobe, eyelids, claws, pads, skin (black, brown, blue, isabella),
- any shade of red,
- there is no darkening on the coat,
- cannot be combined with a mask.
Outwardly distinguish a dog Ay- it is difficult for a red-haired dog to get rid of it. Since within the red range, dogs can breed with each other despite the origin of the red color, this feature is not of great importance.
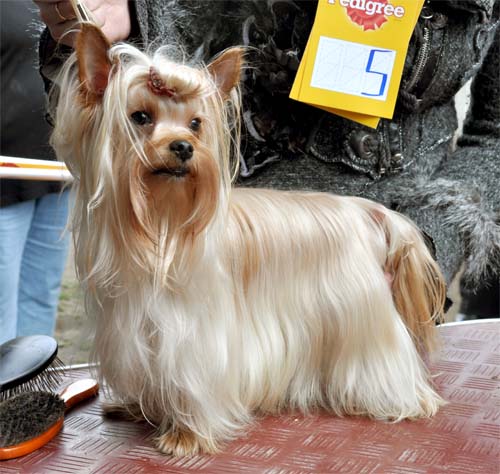


Puppies are born pure red, without darkening. They are described as "cream".
Same dog:
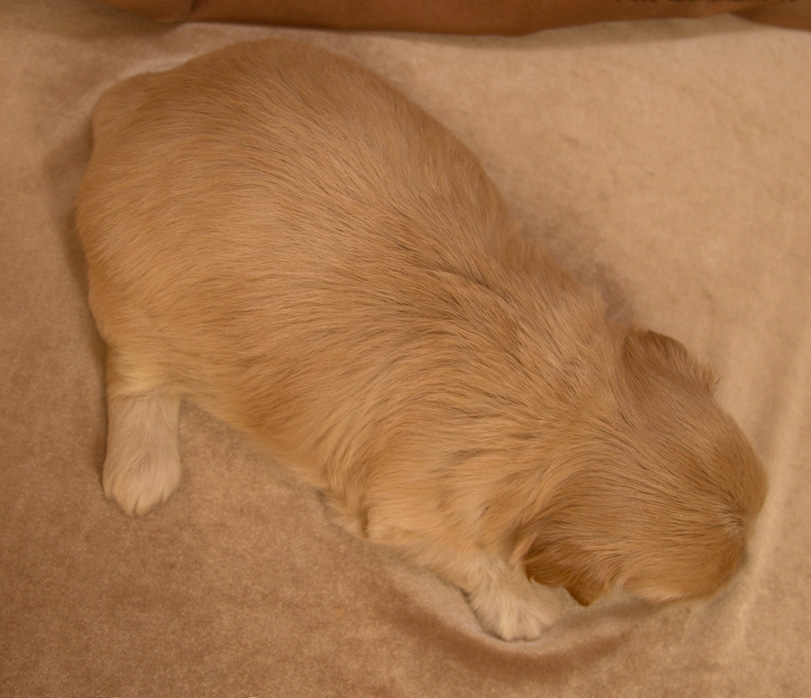
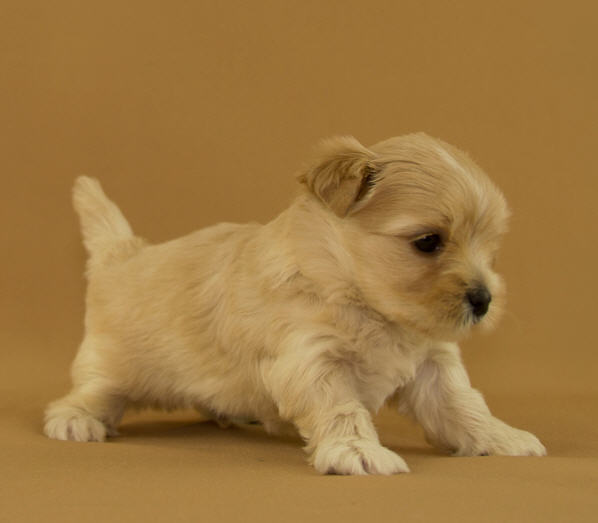
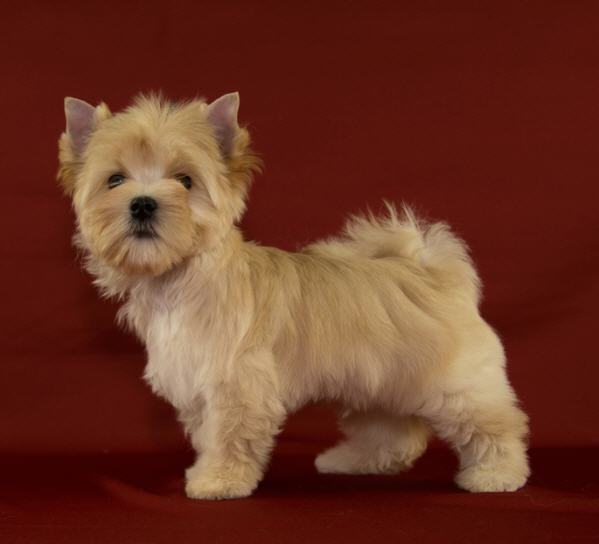



With this color, black/brown pigment (and their weakened variants: blue and isabella) cannot appear in the coat. Black/brown/blue/isabel can only be the nose lobe, mucous membrane, skin, claws, pads. Dogs of this color can have any of the above genes in locus A, but a pair of genes will not allow them to manifest it.
Genotype Variants:
- ee - a completely red dog.
Sometimes it is difficult to determine where the fawn is rich and where the "calm" red. If the breeder finds it difficult to name the color, he should focus on the following features:
- a bright red dog (with or without darkening) is a "redhead";
– a pale red dog (with or without darkening) is a "fawn";
– from two cream dogs (recessive red "ee") puppies are exclusively cream, regardless of the brightness of the red.
FEATURES OF THE RED COLOR
1) The shade of red can be any: from very bright, brick, to very pale, almost white. Preferably, the red pigment should be evenly distributed over the hair: from the base to the tip. And also, the red pigment should be evenly distributed over the entire surface of the dog.
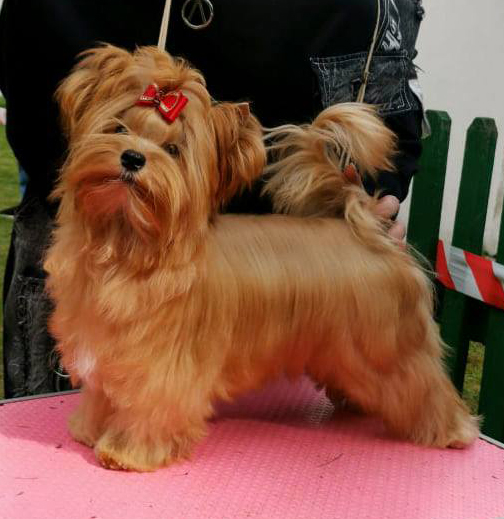



Puppies of any brightness can be born in one litter.
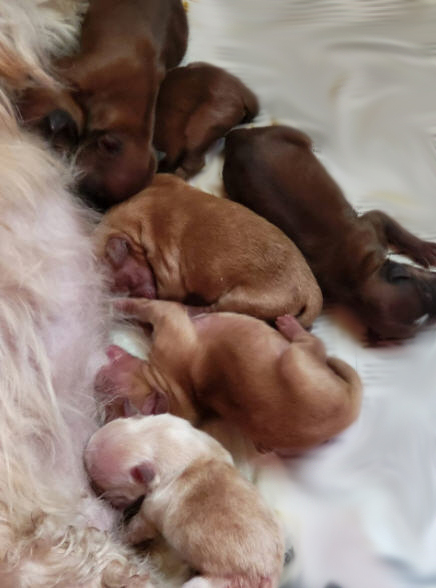


The shade of red can depend on the following factors:
a) the work of the genes of locus I:
— II — rich red color
— II — red color of medium saturation
— ii — lightened shades of red
b) mutations regulating the work of the KITLG gene: this is a variation in the number of copies of DNA (the more of these copies, the more intense the coloration).
2) completely red dogs may have small white spots. At the same time, the volume of white should not exceed 10%. Usually, in such cases, dogs have small white spots in the area of the chin, muzzle, groove between the eyes, throat, chest, fingers and/or on the tip of the tail.
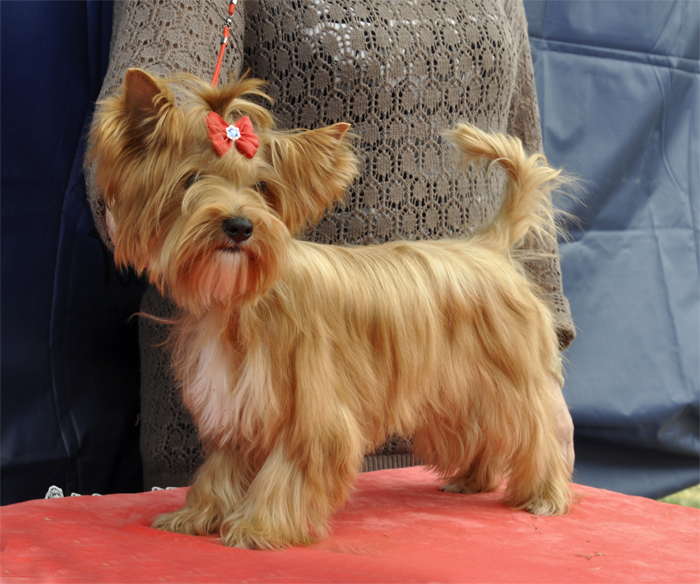


White spot can appear as a result of the following reasons:
- By the time of birth, the pigment has not "had time" to reach certain areas, as a result of which the puppy is born with small white spots on the chin, front of the chest, fingers and/or the tip of the tail. Often such spots are completely painted over, and by the time the puppy is fully red. However, the stain may not be painted over completely.
– as a result of the presence of two genes sisi – Irish spot genes. These genes suggest the presence of white spots in the same areas: chin, front of the chest, fingers, tip of the tail. And they can also appear in the form of white spots on the muzzle and head, grooves between the eyes, collar, pasterns, lower chest.
If the breeder finds it difficult to determine the amount of white, then it is better to act the puppy as "red-white", "fawn-white" or "cream-white".
Examples when determining the name of the color can be difficult
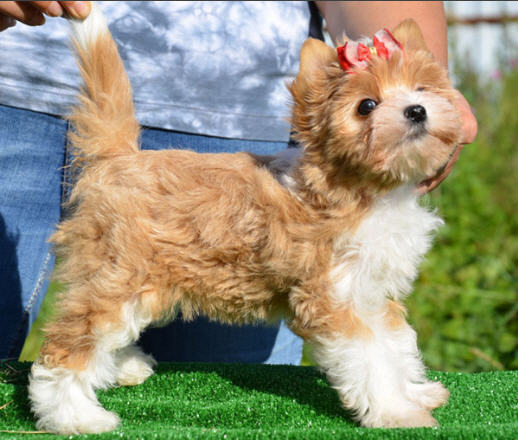


Genotype variants:
— sisi – the dog has white markings between the eyes, on the muzzle, chin, front of the chest, throat, neck, fingers, pasterns and/or the tip of the tail;
— sisw – the dog has white markings in the listed places, carries the piebald gene (large white spots);
—sis – the dog has white markings in the listed places, carries the gene of the extreme degree of pie baldness (almost entirely white dog).
3) sometimes there are darker or lighter areas on the body/head, while the light areas are not the result of white spotting.
In some dogs, sometimes brighter or lighter hair begins to grow from the root, as a result of which "stripes" along the body may appear.
The fur on the muzzle, back and tail is brighter than on the head and skirt

Areas of brighter and less bright fur are visible

There may also be some darker or lighter hair.
4) When bitten by an insect or after injections/vaccinations, a brighter strand may begin to grow in the affected skin area.
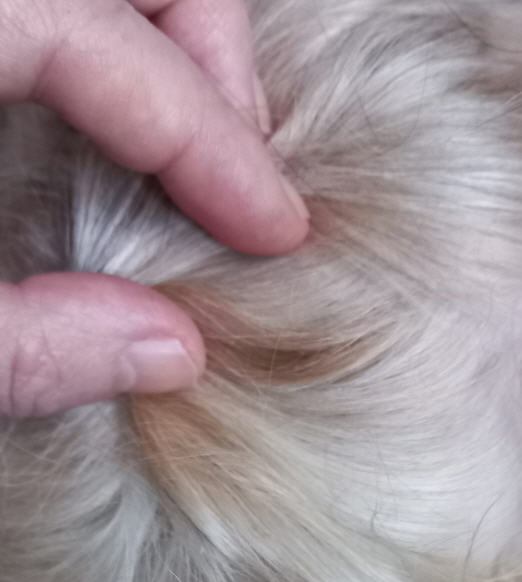
5) dominant red color without darkening (Ayay) and dominant red with darkening (AyatAyatAyatAyatAyat) can be accompanied by a mask. A mask is determined by the presence of a gene Em Em, and can be as bright and deep as you like. The mask can affect the entire muzzle or only the pick-ups. The presence of a mask in the name of the color is not prescribed.
Color with and without a mask has no preference in evaluation.


In many dogs, the mask is observed only at an early age, and when the coat changes, it goes away completely.
Same Dog
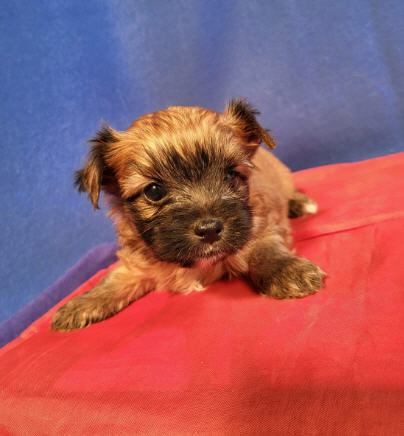
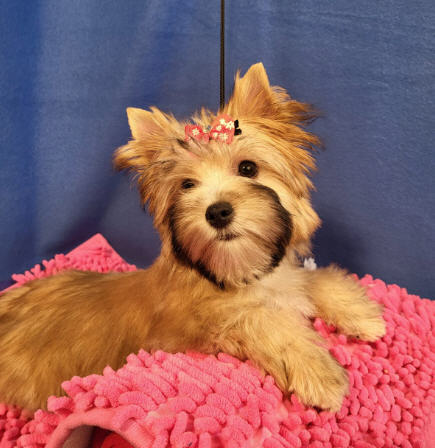


Mask for a newborn fawn puppy.
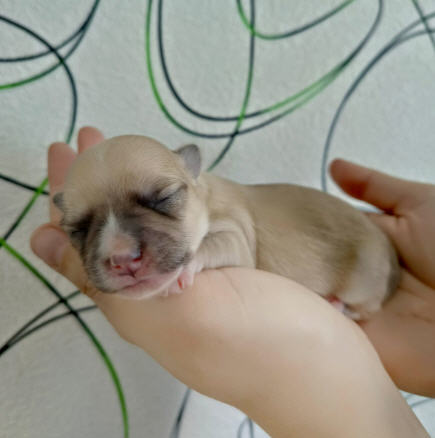

Genotype variants:
— EmEm - a dog with a mask;
— EmE – a dog with a mask, carries the E gene;
— Eme – a dog with a mask, carrying gene e.
6) red pigment can lighten with age: a puppy is born red with a rich shade, but gradually the pigment is produced in smaller quantities. As a result, an adult dog looks like a light redhead.
the same dog at the age of 2 months and 1.5 years


A change in shade can also occur in the opposite direction: a light red puppy can grow into a bright red dog. This is usually seen in cream-colored dogs.
All other things being equal, the most desirable are clean, most saturated and evenly distributed color options over the dog's body.
7) With any red color, there can be under hair. The presence of under hair in the name of the color is not recorded. The under hair is clearly visible at birth and in very young puppies. But gradually the underheard disappears.
Color with and without under hair has no preference in evaluation.
Red puppies with under hair
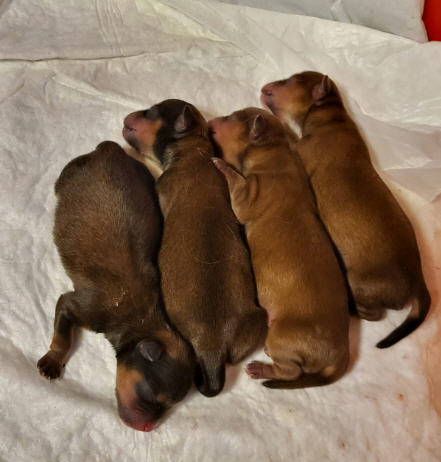

red puppy on the left with a tan
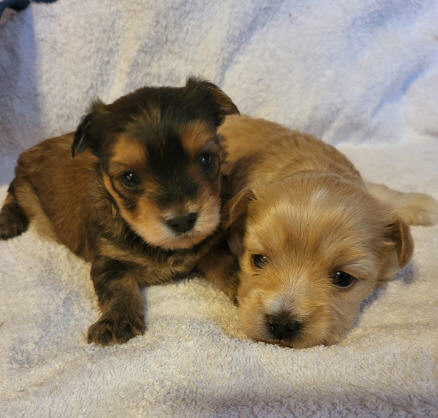

8) With any red color, small puppies can have brown, light brown, blue, bluish-smoky, yellowish eye color (depending on the pigment). If the eye color remains obviously blue/light blue by the time of the acting, such dogs are considered marbled regardless of whether the marble pattern has appeared in the coat.
Spotted Red
All variants of red color can be accompanied by white spots (pie baldness). If the amount of white is more than 10%, such puppies are described as "white-red"/"red-white", "white-fawn"/"fawn-white", "white-cream"/"creamy-white" depending on the area of white.
In Russian salon dogs, any manifestations of white spotting are allowed:
- Irish spot (refers to the "red" color);
- pie baldness;
– extreme degree of pie baldness.
The difference between piebald and extreme piebald is not recorded.
White-red/red-white, white-fawn/fawn-white and white-cream/cream-white dogs belong to the red range, they breed with each other and with redheads.
PIEBALD
A dog is considered piebald if the amount of white is between 10 and 50%. Determined by the presence of a gene sp (locus S).
Genotype variants:
— spsp - piebald dog;
White-red
white and cream

EXTREME DEGREE OF PIEBALD
A dog is considered piebald if the amount of white is more than 50%.
Genotype:
– ss – extreme degree of piebald.
White-red

White-fawn
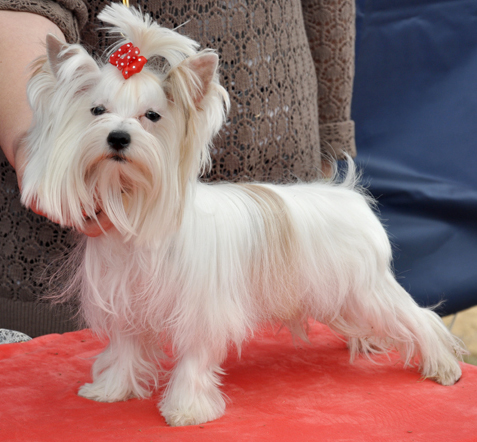

COLOR FEATURES
1) The shade of red can be anything: from very bright, brick, to very pale, almost white.
2) White-red/red-white and white-fawn/fawn-white dogs can be born with darkening on red spots. The darkening can remain or disappear with age, by analogy with a full red color.
3) if the white spot does not lie on the muzzle, then a mask can be observed in white-red/red-white and white-fawn/fawn-white.
4) White-fawn/fawn-white dogs do not have darkening on red spots, do not have a mask on the muzzle.
5) red pigment can lighten with age: a puppy is born with bright red/sable spots, but gradually the pigment is produced in smaller quantities.
Same Dog



Sometimes the lightening is so strong that an adult dog looks almost white.

Dark colors.
"Dark" or "other" colors of Russian salon dogs include:
- black,
- brown,
- blue,
- purple,
- tan,
- brindle,
- marbled
- and their combinations.
All these colors can be of any saturation (any shade).
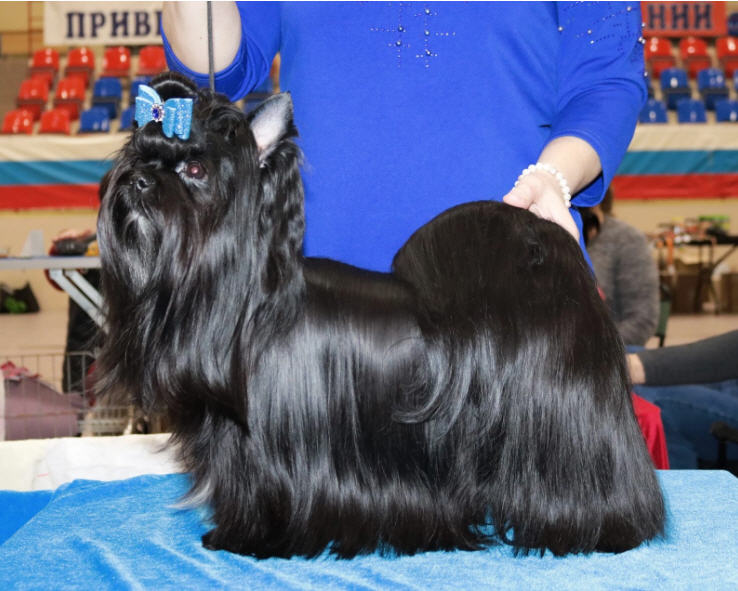
BLACK
Absolute black color can be due to several reasons:
a) the presence of the B gene (locus B)
Genotype variants:
– BB – the dog has a black pigment,
– Bb– the dog has a black pigment, is a carrier of brown pigment.
b) recessive black: due to the presence of two aa genes (locus A);
c) dominant black: due to the presence of the K gene (locus K).
Genotype variants:
– KK – black dog,
– Kkbr – a black dog, carries the gene for brindle,
– Kk – a black dog, carries a gene that allows the production of red pigment in the coat.*
*in some sources – ky.
Outwardly, it is impossible to distinguish recessive black from dominant black. Since black colors can be mated with each other within the variety, there is no fundamental difference between them.


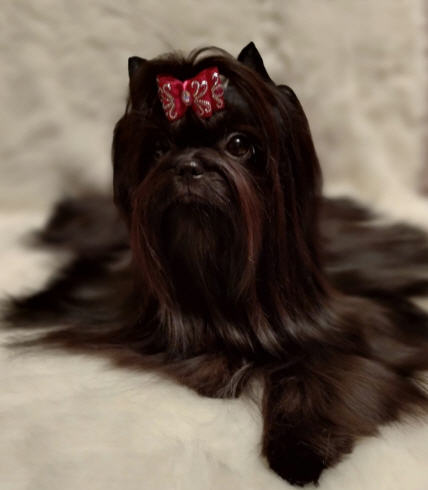
BROWN
Absolute brown color can be due to several reasons:
a) the presence of two bb genes (locus B);
c) dominant brown: due to the presence of the K gene (locus K).
Genotype variants:
– KK – brown dog,
– Kkbr — a brown dog, carries the gene for brindle,
— Kk — a brown dog, carries a gene that allows the production of red pigment in the coat.*
*in some sources — ky.
Externally, it is impossible to distinguish recessive brown from dominant brown. Since within the variety, brown colors can be mated with each other, there is no fundamental difference between them.
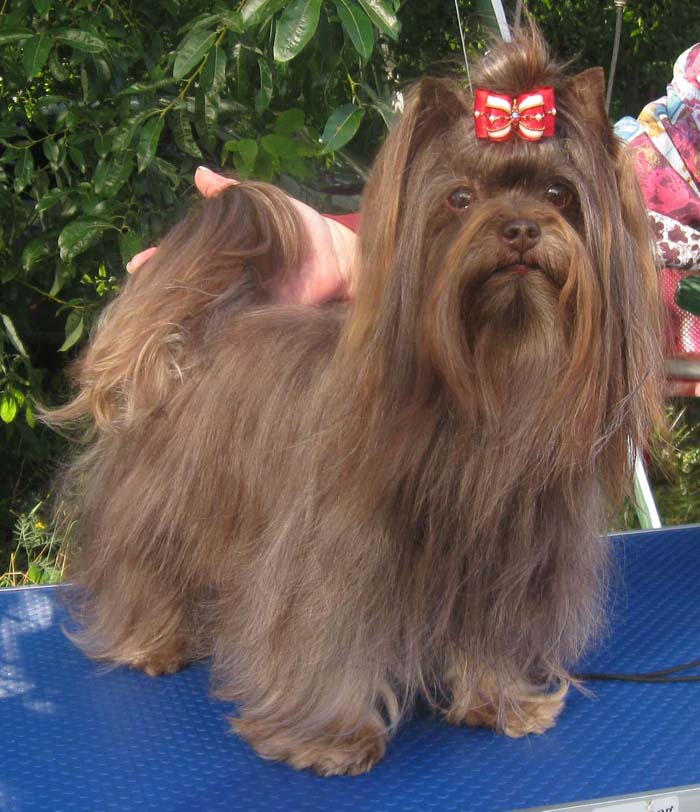


FEATURES OF DARK COLORS
1) With all dark colors, small white spots may be present. At the same time, the volume of white should not exceed 10%. Usually, in such cases, dogs have small white spots in the area of the chin, muzzle, groove between the eyes, throat, chest, fingers and/or on the tip of the tail.
black
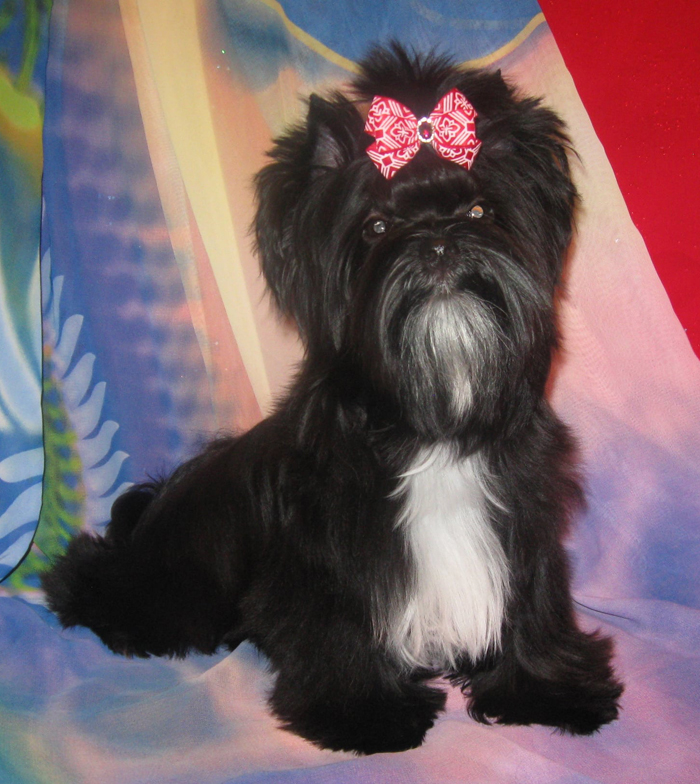

brown
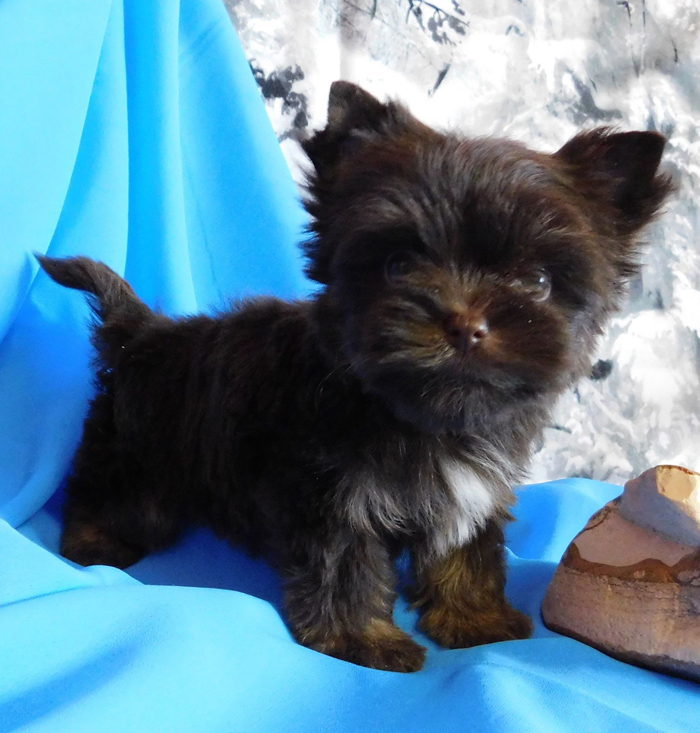

White spotting can appear as a result of the following reasons:
- by the time of birth, the pigment has not "had time" to reach certain areas, as a result of which the puppy is born with small white spots on the chin, front of the chest, fingers and/or the tip of the tail. Often such spots are completely painted over, and by the time the puppy is acted, it is completely black/brown. However, the spot may not be completely painted over.
– as a result of the presence of two genes sisi – Irish spot genes. These genes suggest the presence of white spots in the same areas: chin, front of the chest, fingers, tip of the tail. And they can also appear in the form of white spots on the muzzle and head, grooves between the eyes, collar, pasterns, lower chest.
If the breeder finds it difficult to determine the amount of white, then it is better to act the puppy as black and white, brown and white, etc.

2) Black color can be of any shade (matte black, blue-black), preferably without brownness.
Brown can be of any shade (dark chocolate, light chocolate, coffee with milk, etc.). Dark brown puppies can become lighter with age.
The blue color can be of any shade. A pure gray color, without yellowness, is desirable.
Purple color can be of any shade. A clean saturated shade is desirable.
3) There can be 4 tan colors in the breed:
- black-and-tan,
- brown-tan,
- blue-tan,
- lilac-tan.
Genotype variants:
— atat - a tan dog;
— ata is a tan dog that carries a gene for recessive black/brown color.
black and tan
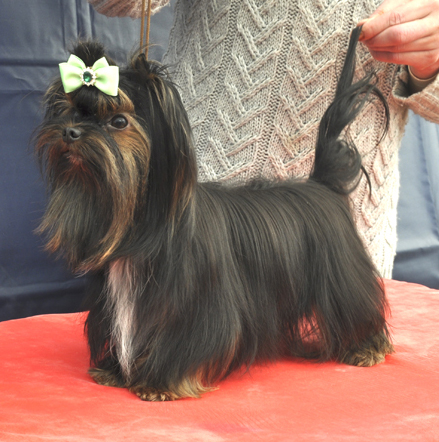

brown and tan

With tan colors, dogs should have red markings in the tan zones:
- on the head: muzzle, cheeks, eyebrows, a strand inside the ear,
- on the throat,
- two spots on the front of the chest,
- on the lower part of all limbs,
- under the tail.
It is desirable that the tan is clearly visible in all the indicated places.
However, sometimes the tan is narrowed:
- all areas of the tan are well manifested, except for one or two,
- all areas of the tan are narrowed to one degree or another, sometimes up to individual hairs. As a result, the dog looks like a completely black/brown/blue/isabella.
In such cases, it is necessary to look for a residual tan between the fingers, under the tail, inside the ear... Even single red hairs in the corresponding areas are a confirmation that this dog is tan.
The tan can also be too extensive: it covers the entire muzzle, the spots on the chest merge into one stripe, the tan on the limbs rises higher, and the tan under the tail covers not only the anus area, but also stretches along the entire underside of the tail. In such cases, it is important that the tan remains within such boundaries that the dog can still be considered tan. Otherwise, the tan can grow further, and the descendants may turn out to be black.
The black color in the breed is considered a pedigree.
The tan can be pure red, or it can be darkened by the main background.
The tan can be of any shade: from pale, gray-white, to bright, brick-red.
Tan puppies can be born with both bright red and pale red tan. The saturation of red can change over time, or it can remain unchanged. The same applies to the area of the tan: puppies can be born both with a tan of the correct pattern and with a narrowed tan. In the latter case, the tan may increase in volume over time, or it may remain the same as at birth for life.
Tan dogs may have a mask that will hide the red zone of the tan on the muzzle. The presence or absence of a mask in the name of the color is not recorded.
With all variants of tan color, there may be brindles on the red zones of the tan, which create the effect of a "smeared", darkened tan. A puppy with brindle tans on the tan is called "brindle-tan", occupying no more than 10%, such a puppy is treated as tan.
If the white is more than 10%, such a puppy is called "white-black-tan", "white-brown-tan", "white-blue-tan", "white-isabella-tan".
All shade options are acceptable.
4) 4 brindle colors are allowed in the breed: The brindle color is due to the presence of a gene kbr.
- black-brindle
- brown-brindle
- blue-brindle
- purple-brindle
Genotype variants:
--kbrkbr – tiger dog,
– kbrk is a brindle dog, carries a gene that allows the production of red pigment in the coat.*
* in some sources — ky.
With brindle coloration, black/brown/blue/purple stripes are observed on a red background.
The red background can be of any shade: from brick red to pale fawn.
Stripes can be
a) arbitrarily wide or narrow. If the stripes are very wide, then the dog looks black with red streaks. If the stripes are very narrow, the dog looks like a red dog with some black streaks,
b) the stripes can cover the entire dog, or they can be single stripes on certain parts of the body/head,
c) the stripes are best seen on short-cut hair, so dogs with a brindle pattern can choose haircuts where the brindle are clearly distinguishable,
d) the stripes are best visible at birth. As the wool grows back, the pattern of the stripes is lost.
Brindle color can be combined with tan color (brindle on a red background tan) and with marbled color (brindle on spots).
If a brindle puppy has white markings that occupy no more than 10%, such a puppy is activated as brindle (black-brindle, brown-brindle, etc.). If the white is more than 10%, such a puppy is called "white-black-brindle", "white-brown-brindle", "white-blue-brindle", "white-purple-brindle".
All variants of brindle are acceptable.
5) 7 marbled colors are allowed:
- black-marble
- brown-marble
- blue-marble
- purple-marble
- red marble
- fawn marble
- cream marble Marble
Marble is due to the presence of the M gene.
Genotype variants:
– MM – marbled dog,
– Mm – marbled dog, carries the gene that allows the birth of a puppy of a non-marbled color.
With a marbled color, ragged black/brown/blue/purple spots are observed on a black/brown/blue/purple background, respectively.
Marbled colors are characterized by the following features:
a) spots are arbitrarily large or small,
b) white spots that are not related to piebald may be observed,
c) a marble pattern may not appear on the coat. Therefore, if one of the parents has any variety of marbled color, and the puppy has not inherited the marbled pattern, then such a puppy must pass a gene test for the carriage of the gene M,
d) the color of the iris with a marbled color can be brown, blue, brown with a blue segment, blue with a brown segment. If a marble pattern has not appeared on the puppy's coat, but there is any manifestation of blue color in the iris, such a puppy is considered marbled,
e) it is desirable to have completely colored eyelids and at least small marks of black/brown/blue/purple pigment on the ears.
Marbled color can be combined with any of the colors available in the breed.
If a marbled puppy has white markings that occupy no more than 10%, such a puppy is described as marbled (black-marble, brown-marbled, etc.).
If the white is more than 10%, such a puppy is described as "white-black-marble", "white-brown-marble", "white-blue-marble", "white-purple-marble".
Marbled dogs can only be bred with non-marbled partners.
All marbled color options are acceptable.
more can be found here Colors of the Russian Salon Dog – kennel "FANN NORD" (funnnord.ru)
full list of colors https://funnnord.ru/okrasy-russkoj-salonnoj-sobaki-nazvaniya-vseh-okrasov/
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.